Note:
This project is almost a two-decade old. If you are an electronics hobbyist, then you may try this. If you are a graduate or postgraduate student, then please try to do a project on some latest technologies.
No more support will be provided for any of these old student-contributed projects. Even you will not get any reply if you raise any query in this regard – sorry.
PLC System
Powerline networks provide the consumer with a low-cost, convenient option for connectivity solutions. As with phone line networks (and other networks using special wires), no antenna or RF conversion hardware is required, making powerline inherently lower in cost than a wireless solution. Using power lines for a home network provides many connection points for network devices.
The AC power line network is a harsh environment for data communication. Brush motors (found in vacuum cleaners), dimmer switches, fluorescent and halogen lights cause interference on the power line. Many outlets on the network have terminating loads of different impedance.
In this project, the possibilities of using power lines for digital data communication is going to be explored. The idea is to connect two distant computers over power-line. To implement the idea a working prototype of a communication system will be designed using components generally available in the electronic market.
Powerline Communication
Efforts to use to the power line as a transmission medium were 160 years ago, but high-speed transmission over 10 Mbps were archived in the mid-1990s. Before this time, the various types of power lines were assumed to be inherently low data rate transfer media.
There are several Powerline Communication (PLC) protocols. The primary purpose of many of these protocols is not for home networking, but rather for powerline control protocols for home automation, home security, and lighting control.
There are powerline control technologies such as X-10, CEBus, and Lonworks. There are also some preliminary high-speed PLC network devices with limited deployment in Europe, where the interest is primarily on access (“last 100 feet”) rather than in-home networks. However, these are expensive and do not enjoy wide use yet; they also must contend with both different regulatory environments and power distribution topologies.
The home network connects to the Internet through a central gateway making the Web accessible at every connection point. Information and peripheral devices can also be shared across the network. Three solutions can be considered for home networking: Ethernet and phone line, wireless, and powerline networks.
Ethernet and phone line solutions provide fast, reliable service but require snaking cable to each connection. Network nodes must be identified and placed during construction of new homes. Considerable renovation is required to retrofit older homes or to place additional nodes.
Wireless networks provide nodes everywhere. They are ideal for hand-held or battery-operated devices, but the addition of RF conversion hardware makes this an inherently costlier solution. Additionally, wireless networks suffer from security concerns and competing standards.
Powerline networking uses power lines existing in the home. Nodes are already available throughout the household, making it a low-cost solution. Each room in a residence possesses one, two, or more outlets.
Any device requiring power will already be attached to the powerline network making it convenient and accessible to low-tech users. Home network users seek three major factors in any solution: ease-of-use, low cost, and ubiquitous node availability. Powerline networking delivers all three. So, while it is true that powerline networking faces some technical hurdles, it remains a compelling choice.
Powerline networks provide the consumer with a low-cost, convenient option for connectivity solutions. As with phone line networks (and other networks using special wires), no antennae or RF conversion hardware is required, making powerline inherently lower in cost than a wireless solution. Using power lines for a home network provides many connection points for network devices.
Applications of Power Line Communication Technology
Nearly all homes and offices have multiple power outlets in every room, and power outlets are all connected together through the electrical wiring already installed in the home. Because it requires no new wiring, and the network adds no cost to your electric bill, Powerline networking is the least expensive method of connecting computers in different rooms. With the explosion of the Internet and broadband technology, power lines present a cost-effective, easy-to-adopt home networking solution for consumers around the globe.
We can categorize the applications of powerline communication system in many ways :
Transfer & share files between computers, such as MP3’s, digital videos, web media and more.
Share an Internet connection with other computers and electronic equipment in the home
Share peripherals such as printers, scanners and cameras
Connect networks
Problem Specification
Using power lines for a home network provides many connection points for network devices. The average Indian home provides probably more connection points versus 1 or 2 phone jacks. As most devices will require a power source, the outlet is a convenient connection point. Powerline networks use a single industry standard to ensure that all powerline network devices will be interoperable.
Several factors present technical challenges to using power lines for data communication. This proposal is able to address these challenges through the unique combination of X10, OFDM, signal coding, and error correction techniques.
Assumptions
In the proposed method of data communication over the power line, we take the following assumptions.
The powerline will be noisy and unreliable for data communication.
The communicating entities are within few hundred meter distance
The communicating entities are within one single transformer limit
For simplicity of design, we assume that there are only two transceivers involved in the communication.
The powerline is assumed as a single phase line.
The Software part of the implementation will be made using Microsoft Visual C++.
The Power line Transceiver Module Design
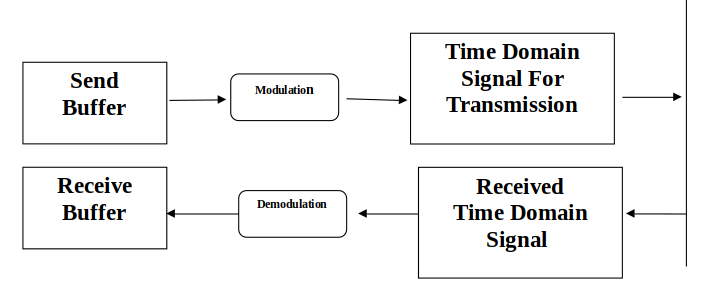
Implementation and Results
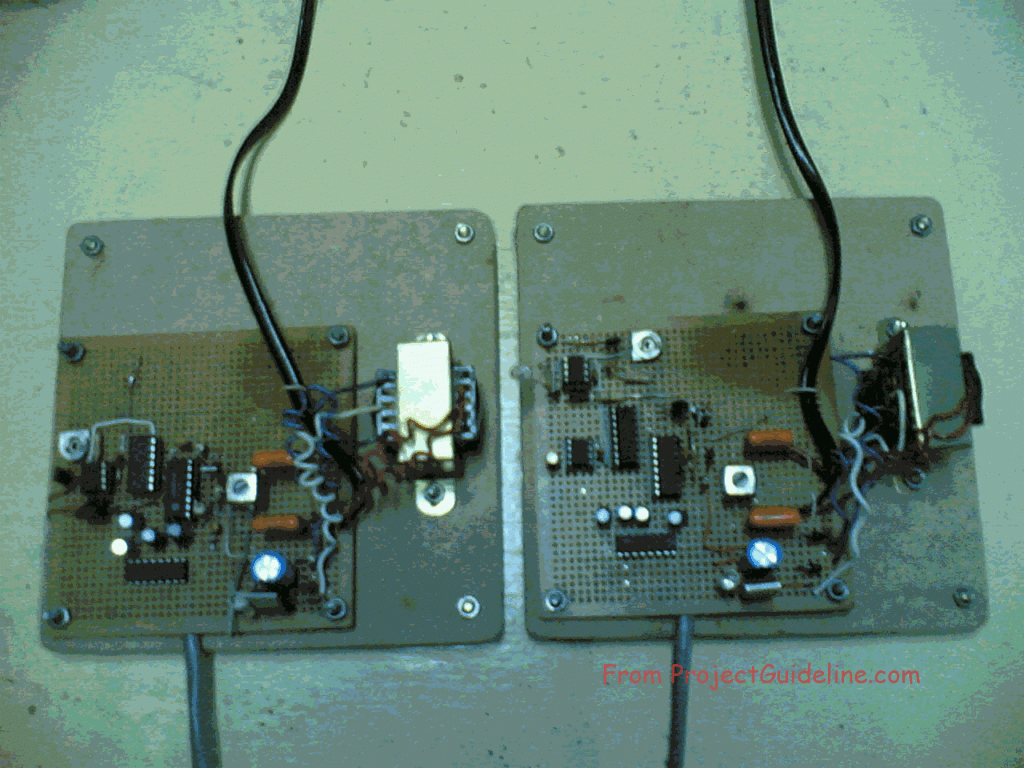
The following picture shows the assebled hardware of PLC data communication system.
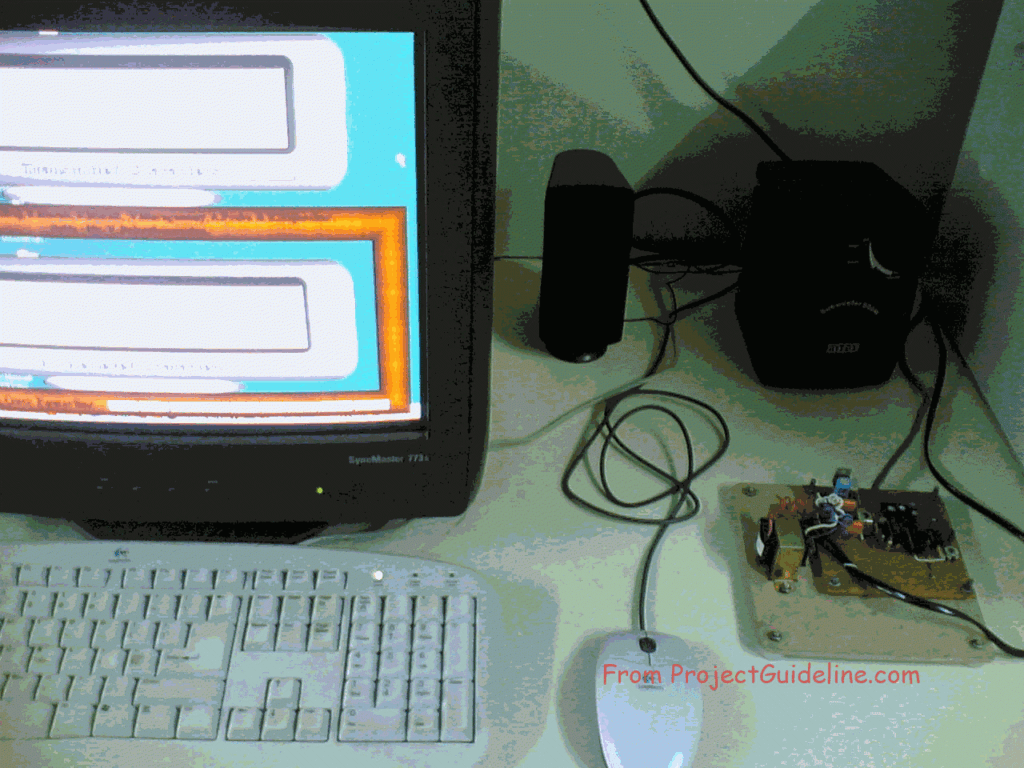
The following picture shows one end of hardware connected with aDesktop PC
The Another End of Hardware Interface Connected with a Desktop PC
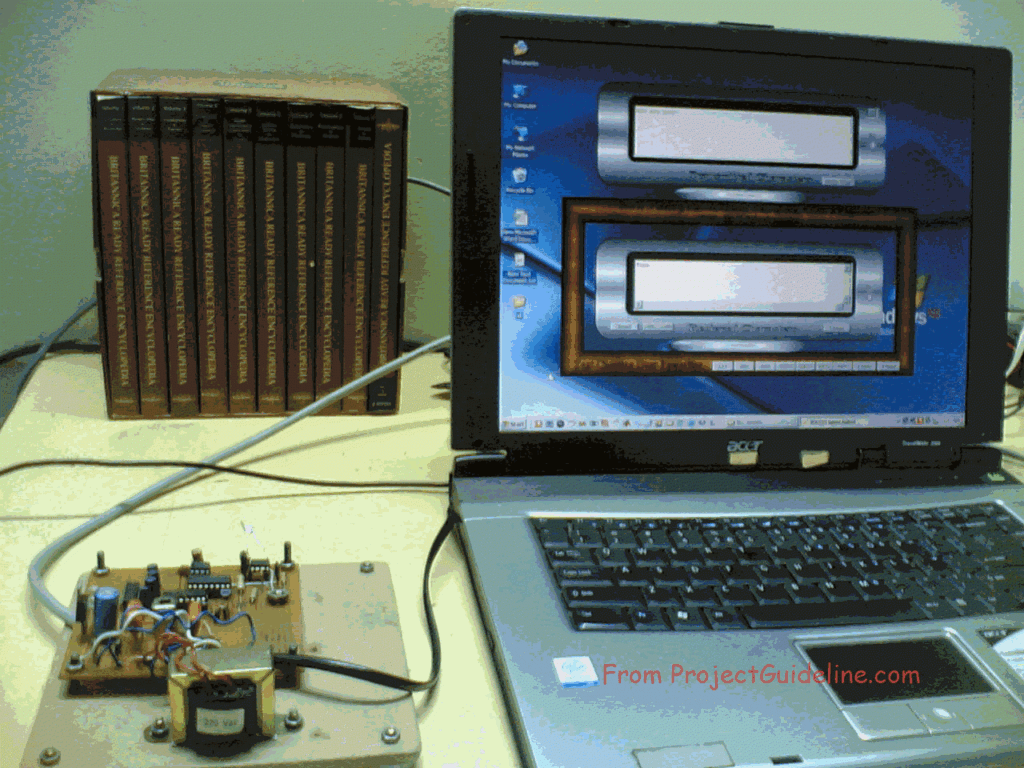
The Another End of the Hardware Interface Connected with a Laptop
The Software Interface
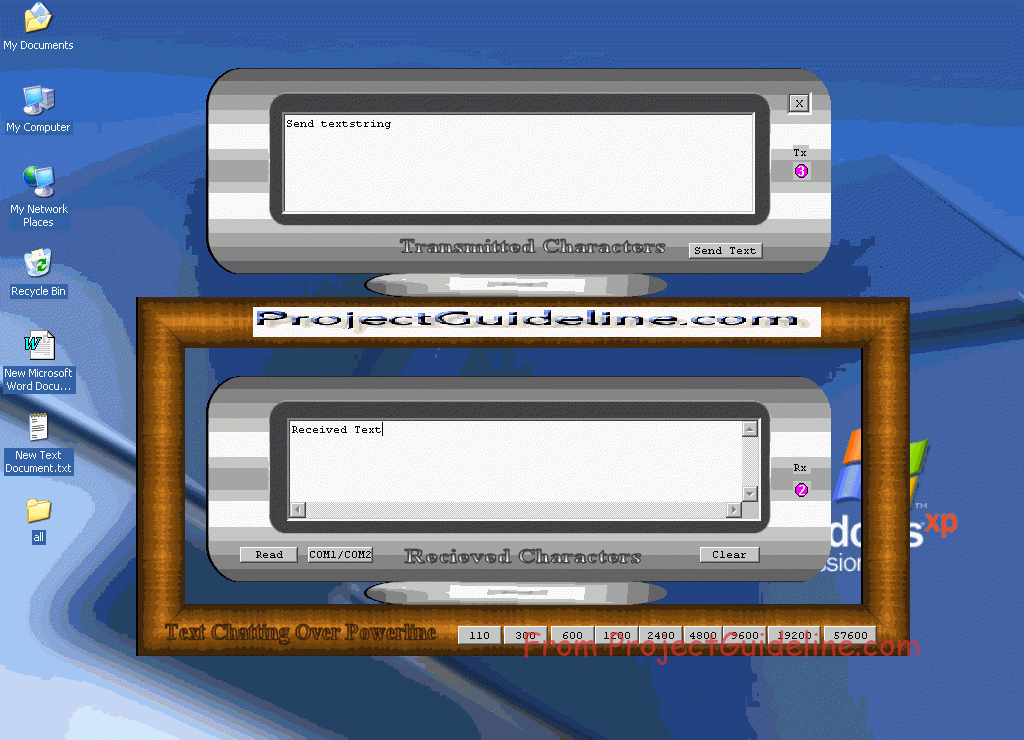
The Tx Window

The Rx Window

Conclusion And Scope for Further Enhancement
The Proposed idea has been successfully implemented and tested on the powerline. A suitable Serial Port Communication software was developed using Microsoft visual C++
Using the powerline network as a data transmission channel does present some technical challenges: multipath distortion effects, noise in the environment, RF interference, and privacy concerns are formidable obstacles. However, the proposed technology is able to manage these concerns with a robust solution that provides reliable data transmission for the simple networking environment. Powerline presents a reliable, low-cost solution for residential networking. This technology can be extended to provides Ethernet-class data networking to support VoIP, QoS, and streaming media applications. Powerline networking turns every AC outlet into a network port. The proposed technology may be well optimized for reliable, high bandwidth network data communication and can also be ported and used in a reliable manner in low-speed devices such as the X10 compatible devices.

 Discuss Through WhatsApp
Discuss Through WhatsApp